- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: CSS
- Hits: 5100
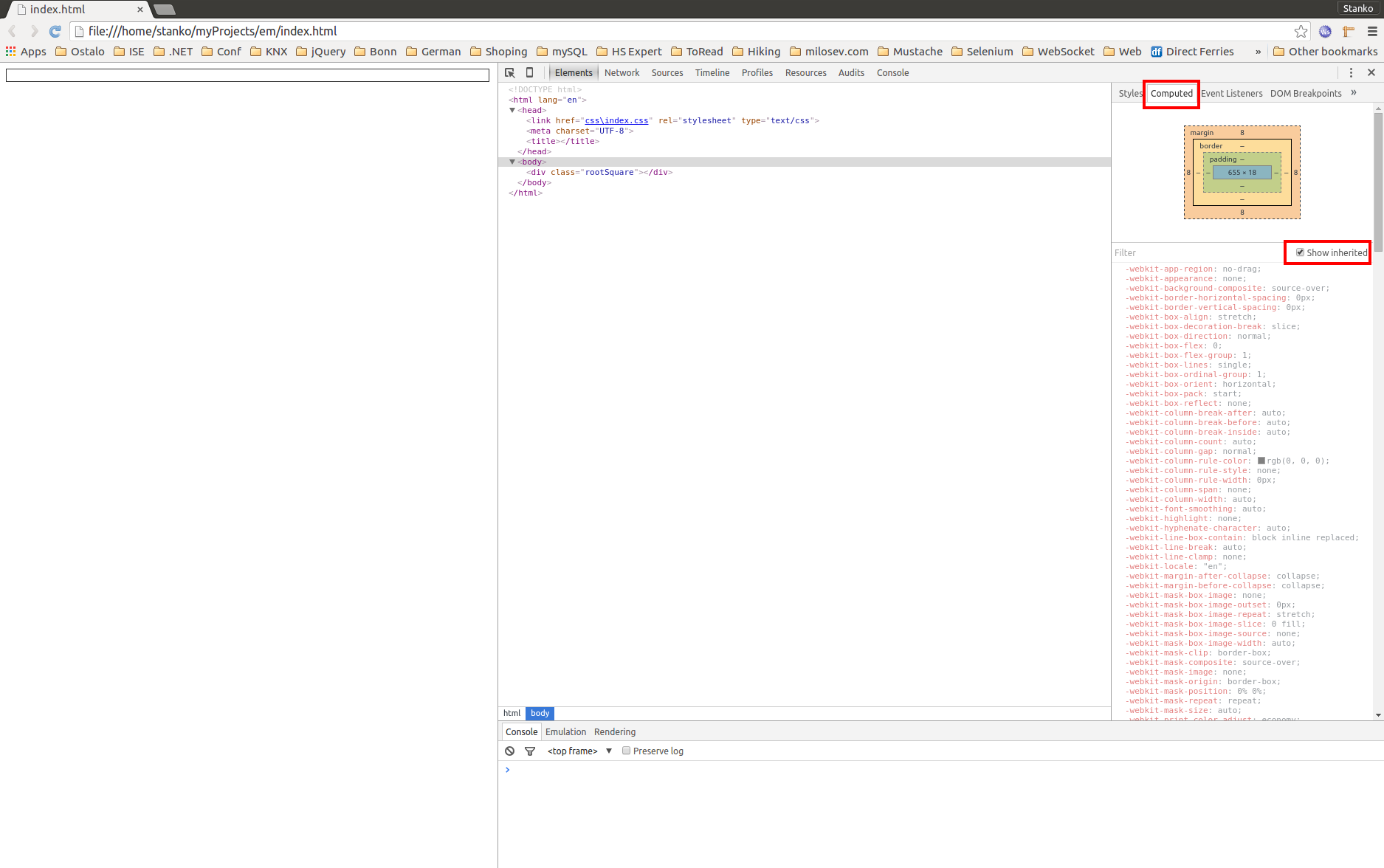
EM - Equal to the computed value of the font-size property of the element on which it is used.
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="rootSquare"></div>
</body>
</html>
CSS:
.rootSquare {
border: 1px solid #333;
height: 1em;
}
Live example:
Notice in this my live example that "rootSquare" div is 14px - that is because parent element's font size is 14 pixels, so that means 1em = parent element font size, if font-size is not defined then default font size is taken
REM - same as the EM the only difference is that it will take font size of the root element which is usually HTML
- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: CSS
- Hits: 5166
Here I mentioned "greater than" (or "bigger than") selector, but while I was reading SMACSS I realized that I don't understand some selectors good enough.
So, here are my examples taken from SMACSS.
Same HTML I am going to use, but with different CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/css/index.css">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="sidebar">
I am a sidebar div
<div>
and I am inner div
<div>
and I am third level div
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
1. With "greater than" selector:
CSS:
#sidebar>div {
border: 1px solid #333;
}
Looks like this:
2. With space
CSS:
#sidebar div {
border: 1px solid #333;
}
Looks like this:
- Details
- Written by: Stanko Milosev
- Category: CSS
- Hits: 11393
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index.css" type="text/css">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="mainContainer">
<div class="subContainer">
<div class="subSubContainer">
<div class="someText">
some text
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
and this CSS:
.mainContainer {
border: 1px solid rgb(0, 0, 0);
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
.subContainer {
border: 1px solid rgb(0, 0, 0);
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
.subSubContainer {
border: 1px solid rgb(0, 0, 0);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: absolute;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
.someText {
left: 18px;
top: 38px;
position: absolute;
}
Live example:
Now we will convert just width and height of subContainer in css to percentage, and formula looks like:
width: calc(100 * 200% / 400);
height: calc(100 * 200% / 400);
Where 200% is 200px from subContainer, 400 is 400px from mainContainer and we multiply it with 100 in order to convert calculation to percentage.
The whole css would look something like:
html, body
{
height: 100%;
}
.mainContainer {
border: 1px solid rgb(0, 0, 0);
width: calc(100*400%/1859);
height: calc(100*400%/1089);
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
.subContainer {
border: 1px solid rgb(0, 0, 0);
width: calc(100 * 200% / 400);
height: calc(100 * 200% / 400);
left: calc(100 * 100% / 400);
top: calc(100 * 100% / 400);
position: absolute;
}
.subSubContainer {
border: 1px solid rgb(0, 0, 0);
width: calc(100 * 100% / 200);
height: calc(100 * 100% / 200);
position: absolute;
left: calc(100 * 50% / 200);
top: calc(100 * 50% / 200);;
}
.someText {
left: 18px;
top: 38px;
position: absolute;
}
Notice that I added:html, body { height: 100%; } and formula to calculate height looks like:
height: calc(100*400%/1089);
Because height of my view port is 1089.